This Climate Bonds briefing focuses mainly on securitisation as a form of financial aggregation and explores how it has been used in the green bond market to date, as well as pointing to potential future developments.
Download the full briefing here.
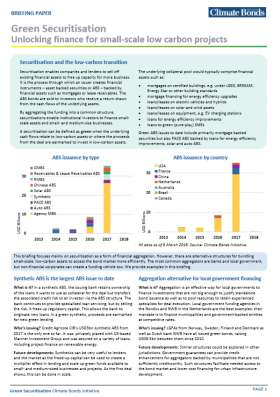
Securitisation enables companies and lenders to sell off existing financial assets to free up capacity for more business. It is the process through which an issuer creates financial instruments – asset backed securities or ABS – backed by financial assets such as mortgages or lease receivables. The ABS bonds are sold to investors who receive a return drawn from the cash flows of the underlying assets.
By aggregating the funding into a common structure, securitisations enable institutional investors to finance smallscale assets and small- and medium-size businesses.
A securitisation can be defined as green when the underlying cash flows relate to low-carbon assets or where the proceeds from the deal are earmarked to invest in low-carbon assets.
There are also alternative structures for bundling small-scale, low-carbon assets to access the bond market more efficiently. The most common aggregators are banks and local government, but non-financial corporates can create a funding vehicle too. We provide examples in this briefing.
Download the full briefing here.